Difference between revisions of "mgh:cyto-1-10"
| Line 451: | Line 451: | ||
* Bile duct epithelium present (except in LCA) | * Bile duct epithelium present (except in LCA) | ||
* Core biopsies provide specific diagnosis: Reticulin stain shows retention of 1 to 2 cells thick hepatic plate framework on cellblock; unpaired arterioles in parenchyma for LCA; bile duct proliferation and scar for FNH | * Core biopsies provide specific diagnosis: Reticulin stain shows retention of 1 to 2 cells thick hepatic plate framework on cellblock; unpaired arterioles in parenchyma for LCA; bile duct proliferation and scar for FNH | ||
| − | + | {{img3|1-10-1 benign_hepatocytes_and_ductal_cells.N12-12133..jpg|1-10-2 reactive_hepatocytes._N12-12133.jpg|Benign hepatocytes and ductal cells|Reactive hepatocytes}} | |
| − | Benign hepatocytes and ductal cells | + | {{img3|1-10-3 reactive_hepatoctes_2.N12-133.jpg|1-10-4 benign_liver_with_reticulin_stain.N12-4918.jpg|Reactive hepatocytes|Benign liver (cirrhosis) with reticulin stain}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Reactive hepatocytes | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Reactive hepatocytes | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Benign liver (cirrhosis) with reticulin stain | ||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
'''Well-differentiated Hepatocellular Carcinoma – N13-6335 and N12-5663''' | '''Well-differentiated Hepatocellular Carcinoma – N13-6335 and N12-5663''' | ||
* Under low power microscopy, smear pattern shows trails of smooth-edged, arborizing clusters of thickened trabeculae with peripheral endothelium (pathognomonic) | * Under low power microscopy, smear pattern shows trails of smooth-edged, arborizing clusters of thickened trabeculae with peripheral endothelium (pathognomonic) | ||
| Line 478: | Line 467: | ||
* α-fetoprotein is helpful if positive but often is not | * α-fetoprotein is helpful if positive but often is not | ||
* Novel markers, such as glypican-3, glutamine synthetase and heat shock protein 70, are helpful if two out of three show positivity | * Novel markers, such as glypican-3, glutamine synthetase and heat shock protein 70, are helpful if two out of three show positivity | ||
| − | + | {{img3|1-10-5 N13-6335.WDHCC.jpg|1-10-6 HCC._reticulin_staining_with_staining_of_thickened_trabeculae.N13-6335..jpg|BWell-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (WDHCC) with peripherally wrapping endothelial cells|WDHCC: reticulin staining showing thickened trabeculae (>3 cells)}} | |
| − | + | {{img3|1-10-7 HCC._reticulin_stain_with_loss_of_staining._N13-6335.jpg|1-10-87 HCC_with_transgressing_vessels._N13-6335..jpg|WDHCC reticulin stain with loss of staining|WDHCC with transgressing, arboring vessels}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | WDHCC: reticulin staining showing thickened trabeculae (>3 cells) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | WDHCC reticulin stain with loss of staining | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | WDHCC with transgressing, arboring vessels | ||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
'''Moderately to Poorly Differentiated Hepatocellular Carcinoma –N12-6639, NC13-322 and N11-12944''' | '''Moderately to Poorly Differentiated Hepatocellular Carcinoma –N12-6639, NC13-322 and N11-12944''' | ||
* Low power smear pattern generally resembles that seen in well-differentiated tumors; however, there is a dyshesive tendency in poorly differentiated tumors | * Low power smear pattern generally resembles that seen in well-differentiated tumors; however, there is a dyshesive tendency in poorly differentiated tumors | ||
| Line 499: | Line 477: | ||
* Polygonal cells with central nuclei and prominent nucleoli with visible, granular to clear cytoplasm in moderately differentiated tumors; scant to no cytoplasm with greater degree of pleomorphism and mitotic activity in poorly differentiated tumors | * Polygonal cells with central nuclei and prominent nucleoli with visible, granular to clear cytoplasm in moderately differentiated tumors; scant to no cytoplasm with greater degree of pleomorphism and mitotic activity in poorly differentiated tumors | ||
* Immunophenotype: low-molecular-weight CK (Cam 5.2), polyclonal carcinoembryonic antigen and CD10 (canalicular), and HepPar-1 and TTF-1 positive; α-fetoprotein variable; high-molecular-weight CK (AE1) negative | * Immunophenotype: low-molecular-weight CK (Cam 5.2), polyclonal carcinoembryonic antigen and CD10 (canalicular), and HepPar-1 and TTF-1 positive; α-fetoprotein variable; high-molecular-weight CK (AE1) negative | ||
| − | + | {{img3|1-10-9 HG_HCC.N12-6639.jpg|1-10-10 HG._HCC.N12-6639.jpg|High grade hepatocellular carcinoma with peripherally-wrapping and arboring vascular pattern; note naked nuclei in the background|High grade hepatocellular carcinoma; note malignant cells making bile}} | |
| − | High grade hepatocellular carcinoma with peripherally-wrapping and arboring vascular pattern; note naked nuclei in the background | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | High grade hepatocellular carcinoma; note malignant cells making bile | ||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
'''Metastatic colonic Adenocarcinoma -- N12-85''' | '''Metastatic colonic Adenocarcinoma -- N12-85''' | ||
* Cigar-shaped, often palisaded nuclei | * Cigar-shaped, often palisaded nuclei | ||
| Line 512: | Line 484: | ||
* Dirty necrosis in the background (key identification point) | * Dirty necrosis in the background (key identification point) | ||
* Immunohistochemistry: CK20 positive, CK7 and CK19 negative, carcinoembryonic antigen positive | * Immunohistochemistry: CK20 positive, CK7 and CK19 negative, carcinoembryonic antigen positive | ||
| − | + | {{img3|1-10-11 Met._colon_cancer.N12-85.jpg|Metastatic colonic adenocarcinoma}} | |
| − | Metastatic colonic adenocarcinoma | ||
| − | |||
{{:mgh:cytology-footer}} | {{:mgh:cytology-footer}} | ||
Revision as of 18:06, July 4, 2020
Contents
The role of fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) in the evaluation of focal liver lesions has evolved bringing with it new challenges.1,2 Advances in dynamic imaging modalities have obviated the need for tissue confirmation in clinically classic cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).3-12 Ultrasound (US) surveillance and serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) assessment of high-risk patients have resulted in the increasing detection of smaller and smaller nodules (≤ 2 cm size).13-16 Accurate cytohistologic characterization of small well-differentiated hepatocellular nodules on limited tissue samples is extremely challenging with therapeutic implications.
Recent years have seen much progress in genomic, microRNA profiling and proteomic studies for the molecular characterization of tumor and peritumoral tissues. They are emerging as promising tools not only in early tumor diagnosis but also for the prediction of HCC behavior in terms of prognosis and progression of disease, and in the development of personalized molecular targeted anticancer therapy and chemopreventive strategies.17-26 As FNAB is currently the most minimally invasive tool for tissue procurement, it is envisaged that FNAB will become a point of care in the management algorithm of HCC for diagnostic, therapeutic and prognostication purposes.27
Guidance Systems
Percutaneous (transabdominal) FNAB performed under ultrasound (US) or computed tomography (CT) guidance is a safe, efficacious and cost-effective outpatient procedure for diagnosis of focal liver lesions.28-30 Aspiration can also be performed at laparotomy or laparoscopy under palpation and/or direct vision. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided FNA (EUS-FNA) is the latest diagnostic and staging tool used primarily for left hepatic lobe lesions and hilar/perihilar masses with the needle traversing the gastrointestinal wall.31 Factors influencing the choice of guidance system include size and location of lesion, operator expertise and preference, and availability of imaging technologies.27-29
Ultrasound provides for rapid localization, flexible patient positioning, and variable imaging of the lesion without radiation. It is generally used for initial guidance, particularly with multiple lesions and/or large, relatively superficial lesions. Computed tomography allows for optimal resolution of small lesions or lesions not visible with US; accurate localization of the needle tip immediately prior to sampling; improved definition of tissue components and vascularity; and more precise demonstration of the anatomic relationships of a given lesion.
EUS-FNA is a safe, accurate and versatile technique but is highly operator-dependent.32-36 It allows for concurrent sampling of pancreas and liver lesions, confirming primary and metastatic malignancy in one single diagnostic encounter. The technique is useful for small and deep-seated left lobe lesions below CT/MRI resolution or not easily accessible by percutaneous FNAB. As such, it enhances staging of liver metastases; is good for early detection of multifocal HCC in cirrhosis; and for assessing the accurate number of lesions (intrahepatic staging of HCC) for transplantation eligibility.37,38
Percutaneous FNAB techniques include individual puncture, coaxial biopsy, and tandem needle biopsy technique.39 Multiple aspirations (up to four passes) can usually be performed with minimal morbidity. The needle size is between 20 to 22G. Aspiration needles with guillotine mechanism enable microbiopsy cores to be procured at the same sitting. Concomitant core needle (18G) biopsies may also be performed. Indications, Contraindications and Complications are outlined in Table 1.
Indications: FNAB is the diagnostic procedure of choice for focal liver lesions, especially to confirm a suspected malignancy. It is particularly advantageous for advanced malignancies and poor surgical candidates. Another indication is drainage of a cyst or abscess for culture and therapeutic ablation.40 An early affirmative diagnosis leads to cost savings in further investigational tests and hospitalization.
Contraindications: Contraindications for percutaneous FNAB include: (i) an uncorrectable bleeding diathesis; (ii) lack of a safe access route, i.e. biopsy through a vascular structure; and (iii) an uncooperative patient in which the need for awkward positioning or maintenance of strict breath control is necessary to assure proper needle placement.28 For EUS-FNA, gastrointestinal obstruction is an absolute contraindication due to risk of perforation.34
Complications: Complications of FNAB are uncommon.39 There may be bleeding - mostly associated with severe cirrhosis with coagulopathy; size of needle used particularly in vascular lesions; and large superficial tumors not covered by normal parenchyma.12 Needle tract seeding is extremely rare (incidence of 0.003 - 0.009% for malignancy in general; and 0.003 - 5% for HCC; if a small (22G), non-cutting needle is used the rate for HCC is around 0.11%).11,41-44 A higher incidence of HCC recurrence in the transplanted liver has been reported in cases with preoperative FNAB.45 Mortality, usually due to bleeding, is rare with a reported rate of 0.018%.42
Clinical Considerations
Much debate surrounds the preoperative FNAB diagnosis of HCC.27
Reasons cited for opposing FNAB include:46-48
• Advances in dynamic imaging modalities are sufficiently sensitive for establishing an HCC diagnosis 3,8,10,11,49
• Risk of needle tract seeding 11,41-44,50
• Risk of intraperitoneal bleeding 12
• Risk of intraprocedural hematogenous dissemination resulting in higher incidence of tumor recurrence and post-transplantation recurrence 41,45
• Adoption of the “wait and see” policy for hepatocellular nodules <1 cm 4,5
• Indeterminate cytohistologic reports rendered for well-differentiated hepatocellular nodules 51,52
Reasons cited for favoring FNAB include:53,54
• Serum alpha-fetoprotein has low sensitivity (<50%) 55,56
• Use of coaxial technique of biopsy may reduce risk of seeding 57
• To cut down on costs of long-term imaging surveillance
• To avoid a futile transplantation in false positive imaging cases 7
• To allay patient anxiety once a liver nodule has been detected on imaging
• Confirmation of HCC increases eligibility for liver transplantation
• For immediate institution of anti-HCC therapy when the lesion is still <2 cm
According to the European Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 2000 Conference (EASL) and American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (AASLD) guidelines, nodules >2 cm in cirrhotic livers are diagnosed as HCC if they show intense arterial profile with contrast washout in delayed venous phase on one dynamic imaging modality.4,5 Nodules between 1 and 2 cm in cirrhotic livers require concurrence of two coincidental imaging modalities; otherwise, biopsy is recommended.49 For nodules <1 cm, the EASL guidelines recommend the “wait and see” policy with 3-monthly US surveillance. It should be noted that about 68% of the nodules <1 cm in cirrhotic livers turn out to be HCCs.58 Ultrasound-guided FNAB of subcentimeter hepatic nodules in skilled hands with expert reader yield correct diagnoses in 90% of cases.41 The conundrum is to balance the risk of unnecessary surgery (2.5%) against the risk of seeding.9,11,53,54
Excerpted from Wee and Pitman. Liver Cytology. Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliart Tract and Pancreas. Odze and Goldblum, eds.
1. Wee A. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatocellular nodular lesions: Role,
controversies and approach to diagnosis. Cytopathology 2011;22:287-305.
2. Fassina A. “The map is not the territory”: FNA the map and liver the territory. Cytopathology 2011;22:285-286.
3. Baron RL, Brancatelli G: Computed tomographic imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004; 127:S133-143.
4. Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM, Beaugrand M, Lencioni R, Burroughs AK, Christensen E, Pagliaro L, Colombo M, Rodes J. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol 2001; 35:421-430.
5. Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2005;42:1208-1236.
6. Caturelli E, Ghittoni G, Roselli P, De Palo M, Anti M. Fine needle biopsy of focal liver lesions: the hepatologist’s point of view. Liver Transpl 2004;10 (2 Suppl 1):S26-29.
7. Durand F,Belghiti J,Paradis V.Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: role of biopsy.Liver Transpl 2007;13 (11 Suppl 2):S17-23.
8. Saar B, Kellner-Weldon F. Radiological diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 2008; 28:189-199.
9. Schőlmerich J, Schacherer D.Diagnostic biopsy for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: useful, necessary, dangerous, or academic sport? Gut 2004;53:1224-1226.
10. Taouli B, Losada M, Holland A, Krinsky G. Magnetic resonance imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004; 127:S144-152.
11. Torzilli G, Minagawa M, Takayama T et al. Accurate preoperative evaluation of liver mass lesions without fine-needle biopsy. Hepatology 1999;30:889–893.
12. Wang P, Meng ZQ, Chen Z et al. Diagnostic value and complications of fine needle aspiration for primary liver cancer and its influence on the treatment outcome. A study based on 3011 patients in China. Eur J Surg Oncol 2008;34:541-546.
13. Daniele B, Bencivenga A, Megna AS, Tinessa V. Alpha-fetoprotein and ultrasonography screening for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004; 127:S108-112.
14. D’Onofrio M, Faccioli N, Zamboni G, Malago R, Caffarri S, Fattovich G, Mucelli RP. Focal liver lesions in cirrhosis: value of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography compared with Doppler ultrasound and alpha-fetoprotein levels. Radiol Med 2008;113:978-991.
15. Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J, Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2003; 362:1907-1917.
16. Bolondi L, Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2003; 39:1076-1084.
17. Hoshida Yet al. Gene expression in fixed tissues and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 2008;359:1995-2004.
18. Ladeiro Y, Couchy G, Balabaud C, Bioulac-Sage P, Pelletier L, Rebouissou S, Zucman-Rossi J.MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations. Hepatology 2008;47:1955-1963
19. Lee JS, Chu IS, Heo J, Calvisi DF, Sun Z, Roskams T, Durnez A, Demetris AJ, Thorgeirsson SS. Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology 2004;40:667-676.
20. Llovet JM et al. A molecular signature to discriminate dysplastic nodules from early hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2006;131: 1758-1767.
21. Malaguarnera G, Giordano M, Paladina I, Berretta M, Cappellani A, Malaguarnera M. Serum markers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 2010; 55:2744-2755.
22. Roncalli M, Park YN, Di Tommaso L. Histopathological classification of hepatocellular carcinoma.Dig Liver Dis 2010;42 (Suppl 3):S228–234.
23. Roskams T, Kojiro M.Pathology of early hepatocellular carcinoma: conventional and molecular diagnosis.Semin Liver Dis 2010;30:17-25.
24. Schroder PC, Segura V, Riezu JI et al. A signature of six genes highlights defects on cell growth and specific metabolic pathways in murine and human hepatocellular carcinoma. Funct Integr Genomics 2011;11:419-429.
25. Wörns M, Galle P. Future perspectives in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis2010;42 (Suppl 3):S302-309.
26. Yamashita T, Forgues M, Wang W, Kim JW, Ye Q, Jia H, Budhu A, Zanetti KA, Chen Y, Qin LX, Tang ZY, Wang XW. EpCAM and alpha-fetoprotein expression defines novel prognostic subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2008;68:1451-1461.
27. Wee A. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of hepatocellular carcinoma and related hepatocellular nodular lesions in cirrhosis: Controversies, challenges, and expectations. Patholog Res Int 2011;2001:587936. Epub 2011 Jun 30.
Guidance systems
28. Moulton JS, Leoni CJ, Quarfordt SD, Worth S. Percutaneous Image-Guided Biopsy. In: Baum S, Pentecost MJ, editors. Abrams' Angiography Interventional Radiology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. p. 257-279.
29. Pitman MB, Szyfelbein WM. Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of the Liver. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1994.
30. Bakshi P, Srinivasan R, Rao KLet al. Fine needle aspiration biopsy in pediatric space-occupying lesions of liver: a retrospective study evaluating its role and diagnostic efficacy. J Pediatr Surg 2006;41:1903-1908.
31. Fritscher-Ravens A, Broering DC, Sriram PVet al. EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration cytodiagnosis of hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a case series. Gastrointest Endosc 2000;52:534-540.
32. Crowe DR, Eloubeidi MA, Chhieng DCet al.Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of hepatic lesions: computerized tomographic-guided versus endoscopic ultrasound guided FNA. Cancer 2006;108:180-185.
33. DeWitt J, LeBlanc J, McHenry Let al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology of solid liver lesions: a large single-center experience. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98:1976-1981.
34. Quirk DM, Brugge WR. Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Directed Fine Needle Aspiration. In: Centeno BA, Pitman MB, editors. Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of the Pancreas. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1999. p. 13-16.
35. Singh P, Erickson RA, Mukhopadhyay Pet al. EUS for detection of the hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;66:265-273.
36. Singh P, Mukhopadhyay P, Bhatt Bet al.Endoscopic ultrasound versus CT scan for detection of the metastases to the liver: results of a prospective comparative study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2009;43:367-373.
37. Awad SS, Fagan S, Abudayyeh Set al. Preoperative evaluation of hepatic lesions for the staging of hepatocellular and metastatic liver carcinoma using endoscopic ultrasonography. Am J Surg 2002;184:601-604.
38. Maheshwari A, Kantsevoy S, Jagannath S, Thuluvath PJ. Endoscopic ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 2010;14:325-332.
39. Strassburg CP, Manns MP. Approaches to liver biopsy techniques--revisited. Semin Liver Dis 2006;26:318-327.
Indications, contraindications, complications
40. Blonski WC, Campbell MS, Faust T, Metz DC. Successful aspiration and ethanol sclerosis of a large, symptomatic, simple liver cyst: case presentation and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:2949-2954.
41. Durand F, Regimbeau JM, Belghiti J et al. Assessment of the benefits and risks of percutaneous biopsy before surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2001;35:254-258.
42. Fornari F, Civardi G, Cavanna L et al. Complications of ultrasonically guided fine-needle abdominal biopsy. Results of a multicenter Italian study and review of the literature. The Cooperative Italian Study Group. Scand J Gastroenterol 1989;24:949-955.
43. Stigliano R, Marelli L, Yu D et al. Seeding following percutaneous diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma. What is the risk and the outcome? Seeding risk for percutaneous approach of HCC. Cancer Treat Rev 2007;33:437-447.
44. Tung WC, Huang YJ, Leung SW et al. Incidence of needle tract seeding and responses of soft tissue metastasis by hepatocellular carcinoma postradiotherapy. Liver Int 2007;27:192-200.
45. Saborido BP, Diaz JC, de Los Galanes SJ et al. Does preoperative fine needle aspiration-biopsy produce tumor recurrence in patients following liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma? Transplant Proc 2005;37:3874-3877.
Controversies
46. Cresswell AB, Welsh FKS, Ree M. A diagnostic paradigm for resectable liver lesions: to biopsy or not to biopsy? HPB (Oxford). 2009;11: 533-540.
47. Hemming AW, Cattral MS, Reed AI et al. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 2001;233:652-659.
48. Stigliano R, Burroughs AK. Should we biopsy each liver mass suspicious for HCC before liver transplantation? – no, please don’t. J Hepatol 2005;43:563-568.
49. Forner A, Vilan R, Ayuso C, Bianchi L, Sole M, Ayuso JR, Boix L, Sala M, Varela M, Llovet JM, Bru C, Bruix J. Diagnosis of hepatic nodules 20 mm or smaller in cirrhosis: Prospective validation of the noninvasive diagnostic criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008;47:97-104.
50. Aldahham A, Boodai S, Alfuderi A, Almosawi A, Asfer S. Abdominal wall implantation of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol 2006;4:72.
51. de Boer WB, Segal A, Frost FA, Sterrett GF. Cytodiagnosis of well differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma: can indeterminate diagnoses be reduced? Cancer (Cancer Cytopathol) 1999;87:270-277.
52. Wee A, Nilsson B. Highly well differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma and benign hepatocellular lesions. Can they be distinguished on fine needle aspiration biopsy? Acta Cytol 2003;47:16-26.
53. Chapoutot C, Perney P, Fabre D et al. Needle-tract seeding after ultrasound-guided puncture of hepatocellular carcinoma. A study of 150 patients. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 1999;23:552–556.
54. Ng KK, Poon RT, Lo CM et al. Impact of preoperative fine-needle aspiration cytologic examination on clinical outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a tertiary referral center. Arch Surg 2004;139:193–200.
55. Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis: The demise of a brilliant star. Gastroenterology 2009;137:26-29.
56. Sherman M: Alphafetoprotein: an obituary. J Hepatol 2001; 34:603-605.
57. Maturen KE, Nghiem HV, Marrero JA et al. Lack of tumor seeding of hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous needle biopsy using coaxial cutting needle technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006;187:1184-1187.
58. Caturelli E, Solmi L, Anti M et al. Ultrasoundguided fine needle biopsy of early hepatocellular carcinoma complicatingliver cirrhosis: a multicentre study. Gut 2004;53:1356-1362.
Procurement Methods for Liver FNAB
Guidance Systems
Percutaneous (transabdominal) FNAB performed under ultrasound (US) or computed tomography (CT) guidance is a safe, efficacious and cost-effective outpatient procedure for diagnosis of focal liver lesions.28-30 Aspiration can also be performed at laparotomy or laparoscopy under palpation and/or direct vision. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided FNA (EUS-FNA) is the latest diagnostic and staging tool used primarily for left hepatic lobe lesions and hilar/perihilar masses with the needle traversing the gastrointestinal wall.31 Factors influencing the choice of guidance system include size and location of lesion, operator expertise and preference, and availability of imaging technologies.27-29
Ultrasound provides for rapid localization, flexible patient positioning, and variable imaging of the lesion without radiation. It is generally used for initial guidance, particularly with multiple lesions and/or large, relatively superficial lesions. Computed tomography allows for optimal resolution of small lesions or lesions not visible with US; accurate localization of the needle tip immediately prior to sampling; improved definition of tissue components and vascularity; and more precise demonstration of the anatomic relationships of a given lesion.
EUS-FNA is a safe, accurate and versatile technique but is highly operator-dependent.32-36 It allows for concurrent sampling of pancreas and liver lesions, confirming primary and metastatic malignancy in one single diagnostic encounter. The technique is useful for small and deep-seated left lobe lesions below CT/MRI resolution or not easily accessible by percutaneous FNAB. As such, it enhances staging of liver metastases; is good for early detection of multifocal HCC in cirrhosis; and for assessing the accurate number of lesions (intrahepatic staging of HCC) for transplantation eligibility.37,38
Percutaneous FNAB techniques include individual puncture, coaxial biopsy, and tandem needle biopsy technique.39 Multiple aspirations (up to four passes) can usually be performed with minimal morbidity. The needle size is between 20 to 22G. Aspiration needles with guillotine mechanism enable microbiopsy cores to be procured at the same sitting. Concomitant core needle (18G) biopsies may also be performed. Indications, Contraindications and Complications are outlined in Table 1.
Indications: FNAB is the diagnostic procedure of choice for focal liver lesions, especially to confirm a suspected malignancy. It is particularly advantageous for advanced malignancies and poor surgical candidates. Another indication is drainage of a cyst or abscess for culture and therapeutic ablation.40 An early affirmative diagnosis leads to cost savings in further investigational tests and hospitalization.
Contraindications: Contraindications for percutaneous FNAB include: (i) an uncorrectable bleeding diathesis; (ii) lack of a safe access route, i.e. biopsy through a vascular structure; and (iii) an uncooperative patient in which the need for awkward positioning or maintenance of strict breath control is necessary to assure proper needle placement.28 For EUS-FNA, gastrointestinal obstruction is an absolute contraindication due to risk of perforation.34
Complications: Complications of FNAB are uncommon.39 There may be bleeding - mostly associated with severe cirrhosis with coagulopathy; size of needle used particularly in vascular lesions; and large superficial tumors not covered by normal parenchyma.12 Needle tract seeding is extremely rare (incidence of 0.003 - 0.009% for malignancy in general; and 0.003 - 5% for HCC; if a small (22G), non-cutting needle is used the rate for HCC is around 0.11%).11,41-44 A higher incidence of HCC recurrence in the transplanted liver has been reported in cases with preoperative FNAB.45 Mortality, usually due to bleeding, is rare with a reported rate of 0.018%.42
Excerpted from Wee and Pitman. Liver Cytology. Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliart Tract and Pancreas. Odze and Goldblum, eds.
Guidance systems
1. Moulton JS, Leoni CJ, Quarfordt SD, Worth S. Percutaneous Image-Guided Biopsy. In: Baum S, Pentecost MJ, editors. Abrams' Angiography Interventional Radiology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. p. 257-279.
2. Pitman MB, Szyfelbein WM. Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of the Liver. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1994.
3. Bakshi P, Srinivasan R, Rao KLet al. Fine needle aspiration biopsy in pediatric space-occupying lesions of liver: a retrospective study evaluating its role and diagnostic efficacy. J Pediatr Surg 2006;41:1903-1908.
4. Fritscher-Ravens A, Broering DC, Sriram PVet al. EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration cytodiagnosis of hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a case series. Gastrointest Endosc 2000;52:534-540.
5. Crowe DR, Eloubeidi MA, Chhieng DCet al.Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of hepatic lesions: computerized tomographic-guided versus endoscopic ultrasound guided FNA. Cancer 2006;108:180-185.
6. DeWitt J, LeBlanc J, McHenry Let al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology of solid liver lesions: a large single-center experience. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98:1976-1981.
7. Quirk DM, Brugge WR. Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Directed Fine Needle Aspiration. In: Centeno BA, Pitman MB, editors. Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of the Pancreas. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1999. p. 13-16.
8. Singh P, Erickson RA, Mukhopadhyay Pet al. EUS for detection of the hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;66:265-273.
9. Singh P, Mukhopadhyay P, Bhatt Bet al.Endoscopic ultrasound versus CT scan for detection of the metastases to the liver: results of a prospective comparative study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2009;43:367-373.
10. Awad SS, Fagan S, Abudayyeh Set al. Preoperative evaluation of hepatic lesions for the staging of hepatocellular and metastatic liver carcinoma using endoscopic ultrasonography. Am J Surg 2002;184:601-604.
11. Maheshwari A, Kantsevoy S, Jagannath S, Thuluvath PJ. Endoscopic ultrasound and fine-needle aspiration for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 2010;14:325-332.
12. Strassburg CP, Manns MP. Approaches to liver biopsy techniques--revisited. Semin Liver Dis 2006;26:318-327.
Indications, contraindications, complications
13. Blonski WC, Campbell MS, Faust T, Metz DC. Successful aspiration and ethanol sclerosis of a large, symptomatic, simple liver cyst: case presentation and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:2949-2954.
14. Durand F, Regimbeau JM, Belghiti J et al. Assessment of the benefits and risks of percutaneous biopsy before surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2001;35:254-258.
15. Fornari F, Civardi G, Cavanna L et al. Complications of ultrasonically guided fine-needle abdominal biopsy. Results of a multicenter Italian study and review of the literature. The Cooperative Italian Study Group. Scand J Gastroenterol 1989;24:949-955.
16. Stigliano R, Marelli L, Yu D et al. Seeding following percutaneous diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma. What is the risk and the outcome? Seeding risk for percutaneous approach of HCC. Cancer Treat Rev 2007;33:437-447.
17. Tung WC, Huang YJ, Leung SW et al. Incidence of needle tract seeding and responses of soft tissue metastasis by hepatocellular carcinoma postradiotherapy. Liver Int 2007;27:192-200.
18. Saborido BP, Diaz JC, de Los Galanes SJ et al. Does preoperative fine needle aspiration-biopsy produce tumor recurrence in patients following liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma? Transplant Proc 2005;37:3874-3877.
Test Platform and Processing
The types of small tissue samples from liver FNAB include direct smears, needle rinses, core imprints, cellblocks, microbiopsies and core needle biopsies. Smears may be air-dried and stained with Diff-Quik® and/or May-Grϋnwald-Giemsa (MGG), and/or fixed in 95% alcohol and stained by the Papanicolaou method. Rapid touch prep core imprints can be performed to assess adequacy of tissue cores.1 If well-fixed, adequately smeared slides are difficult to obtain, the aspirate can be expressed into a preservative and submitted as a liquid-based specimen for processing by either the ThinPrep® or Sure Path™ methods.
Cellblocks are made from needle rinses and tissue fragments.2,3 Particulate material should be quickly retrieved from the glass slides prior to staining for formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded cellblock preparation. Histologic sections allow for architectural appraisal, special stains and immunohistochemistry. Immunocytochemistry may be necessary if only smears are available.
Excerpted from Wee and Pitman. Liver Cytology. Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliart Tract and Pancreas. Odze and Goldblum, eds.
1. Hahn PF, Eisenberg PJ, Pitman MB, Gazelle GS, Mueller PR. Cytopathologic touch preparations (imprints) from core needle biopsies: accuracy compared with that of fine-needle aspirates. AJR 1995;165:1277-1279.
2. Ceyhan K, Kupana SA, Bektas Met al. The diagnostic value of on-site cytopathological evaluation and cell block preparation in fine-needle aspiration cytology of liver masses. Cytopathology 2006;17:267-274.
3. Wee A. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of the liver: Algorithmic approach and current issues in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cytojournal 2005;2:7.
Reporting and Terminology
Focal liver lesions range from cystic and inflammatory/infectious entities to benign/malignant, primary/metastatic neoplasms. HCC is well-known for its heterogeneity. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (CC) frequently has nondescript adenocarcinoma features. The liver is a common depository for metastases. Given these permutations, one has to recognize that primary liver carcinomas can mimic many tumors, and vice versa. The diagnostic issues are listed below:
Diagnostic Issues in Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy Evaluation of Focal Liver Lesions
• To distinguish well-differentiated hepatocellular nodules from reactive hepatocytes
• To distinguish between the various types of benign well-differentiated hepatocellular nodules
• To distinguish early well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma from benign hepatocellular nodules
• To distinguish poorly differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
• To distinguish intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma from metastatic adenocarcinomas
• To distinguish poorly differentiated primary liver carcinomas from metastases
• To ascertain the histogenesis of a non-hepatocellular tumors
• To ascertain the primary site of origin of a malignant non-hepatocellular tumors
• To differentiate between benign and malignant cystic lesions
• To recognize inflammatory/infectious lesions that may mimic tumors
Integrative Approach to the Evaluation of Liver Aspirates
A stepwise algorithmic approach incorporating full clinicopathologic correlation is of utmost importance.1
Step 1: Evaluate clinical information
A patient may present with one or more focal liver lesions under the following scenarios: (i) Routine medical checkup, (ii) Screening or surveillance for chronic liver disease, (iii) Follow-up of known cancer case, (iv) Investigation of symptomatic patient, or (v) Investigation of pediatric lesion. Relevant clinical findings, liver function profile, serology and tumor markers should be sought.2-4
Step 2: Evaluate radiologic information
The focal liver lesion may be cystic or solid, single or multiple. Evidence of pre-existing or chronic hepatobiliary disease and other relevant associated radiologic findings should be sought. Advances in dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging modalities have increased the sensitivity and specificity for the detection of classic HCC. Siderotic nodules are readily detected on T2 -orT2* weighted MR imaging.3
Step 3: Evaluate cytohistologc findings
Scan the smears at low power to establish the pattern and architecture before closer scrutiny for cellular details as listed in Table 5. One should ascertain whether the lesion is: (i) cystic – true cyst or pseudocyst, benign or malignant; or (ii) solid – hepatocellular or non-hepatocellular, benign or malignant. The diagnostic algorithms for the evaluation of cystic and solid lesions of the liver are below:
Diagnostic Algorithm of Cystic Lesions of the Liver (modified from WHO Classification of Tumors of the Digestive System, 4th edition, 2010)4
I. Cystic lesion with epithelial lining
a. Cuboidal / low columnar epithelium: Solitary bile duct cyst, fibropolycystic disease and obstructive dilatation of bile duct
b. Ciliated epithelium: Ciliated foregut cyst
c. Biliary / mucinous / oncocytic (+/- papillae):
(i) With ovarian-like stroma
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm with low-, intermediate- or high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm with an associated invasive carcinoma
(ii) Without ovarian-like stroma
- Biliary intraductal papillary neoplasm with low-, intermediate- or high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia
- Biliary intraductal papillary neoplasm with an associated invasive carcinoma
d. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with cystic change; arising from malignant transformation in pre-existing cystic disease; or associated with cystically dilated bile ducts
e. Metastases
II. Cystic lesion without epithelial lining
a. Neoplastic (including tumor-like lesions):
(i) Cavernous hemangioma
(ii) Mesenchymal hamartoma
(iii) Cystic degeneration in any benign or malignant tumor
(iv) Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma
b. Nonneoplastic
(i) Laminated wall: Hydatid cyst
(ii) Inflammation and necrosis: Pyogenic / fungal / amebic abscess, granulomas, necrotizing eosinophilic granuloma, hydatid cyst
(iii) Hemorrhagic cyst: Cystic hematoma
Diagnostic Algorithm of Solid Lesions of the Liver
I. Hepatocellular appearance
a. Focal fatty change
b. Large regenerative nodule
c. Dysplastic nodule, low- or high-grade
d. Siderotic nodule (regenerative, dysplastic)
e. Focal nodular hyperplasia
f. Hepatocellular adenoma
g. Hepatocellular carcinoma, variants and special types
h. Hepatoblastoma
II. Hepatocellular and glandular appearance
a. Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
III. Non-hepatocellular appearance
a. Glandular pattern: Bile duct adenoma (peribiliary gland hamartoma), intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma, metastases
b. Squamous, including adenosquamous, pattern: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, metastases
c. Mucinous pattern: Mucinous cystic neoplasm, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, metastases
d. Papillary pattern: Intraductal papillary neoplasm, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, metastases
e. Clear cell pattern: Angiomyolipoma, metastases (renal cell carcinoma, adrenocortical carcinoma)
f. Oncocytic cell pattern: Angiomyolipoma, metastases (renal cell carcinoma, adrenocortical carcinoma), melanoma
g. Small cell pattern: Neuroendocrine tumor, lymphoma, metastases (small cell carcinoma, lobular carcinoma of breast, melanoma), inflammatory pseudotumor
h. Large cell pattern: Neuroendocrine carcinoma, metastases (undifferentiated carcinoma)
i. Spindle cell pattern: Cavernous hemangioma, infantile hemangioma, solitary fibrous tumor, inflammatory pseudotumor, angiomyolipoma, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, sarcomatoid carcinoma (including primary liver carcinomas and metastatic sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma), sarcoma (primary and metastatic, including angiosarcoma, Kaposi sarcoma, carcinosarcoma, hepatobiliary rhabdomyosarcoma, synovial sarcoma and leiomyosarcoma)
j. Giant cell pattern: Sarcomatoid/giant cell carcinoma (primary liver carcinomas and metastases), sarcoma (primary and metastases)
k. Others: Nodular hematopoiesis, epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, germ cell tumors (teratoma and yolk sac tumor)
Step 4: Evaluate ancillary studies
The initial cytomorphologic impression is crucial as the material available usually limits the choice of immunohistochemical and other ancillary tests.
Step 5: Correlate all of above
Clinicopathologic correlation is mandatory for the final definitive diagnosis. An indeterminate diagnosis may be rendered for highly well-differentiated hepatocellular nodules. Information gleaned from all the above, including a complete immunohistochemical workup, may only help establish a generic morphologic diagnosis for non-hepatocellular lesions but not the organ of origin.
Excerpted from Wee and Pitman. Liver Cytology. Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliart Tract and Pancreas. Odze and Goldblum, eds.
1. Wee A and P Sampatanukul. Fine needle aspiration cytology of the liver. Diagnostic Algorithms. A Southeast Asian perspective. Bangkok: Year Book Publisher Co., Ltd, 2004.
2. Zhang J, Krinsky GA. Iron-containing nodules of cirrhosis. NMR Biomed 2004;17:459-464.
3. Krinsky GA, Lee VS, Nguyen MT et al. Siderotic nodules at MR imaging: regenerative or dysplastic? J Comput Assist Tomogr 2000;24:773-776.
4. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND (Eds.). WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System. IARC: Lyon 2010
Basic cytomorphology
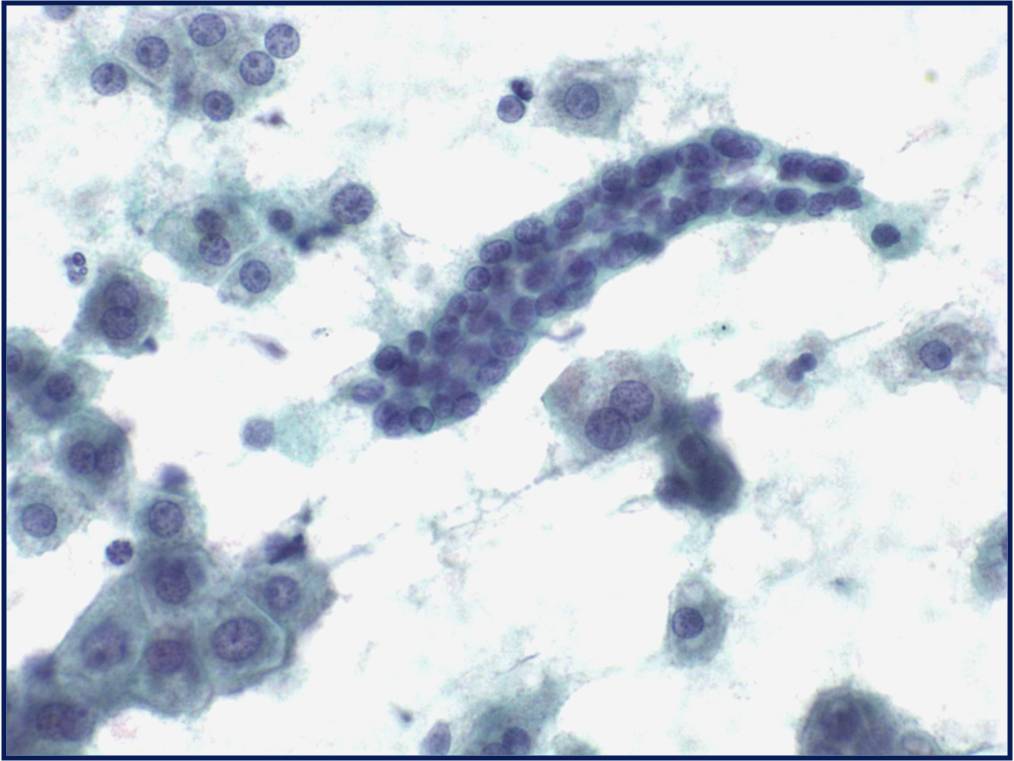
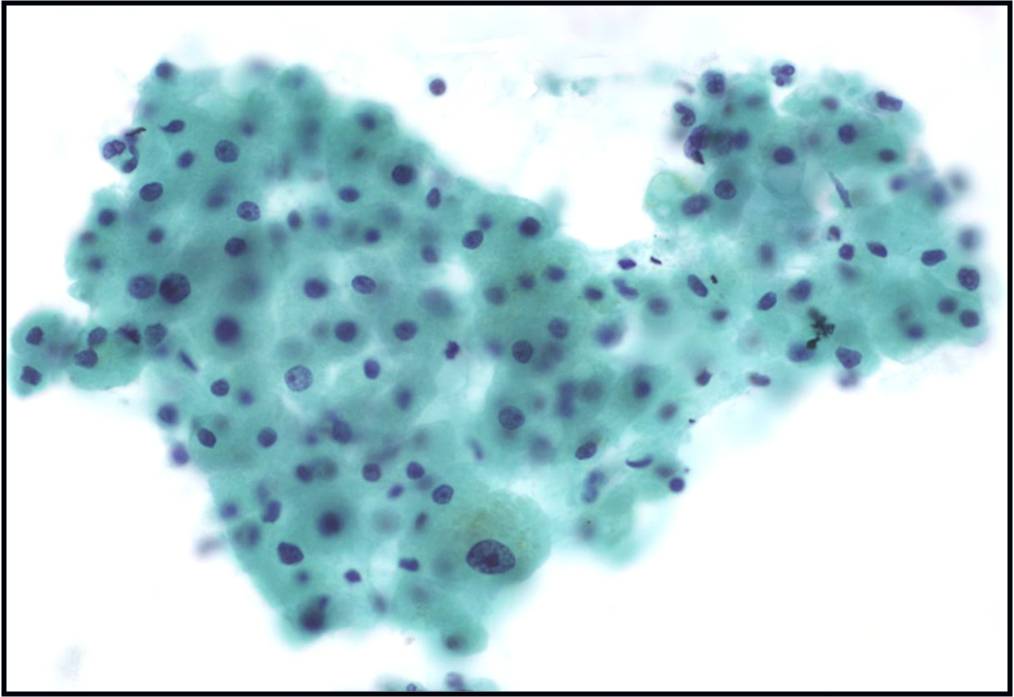
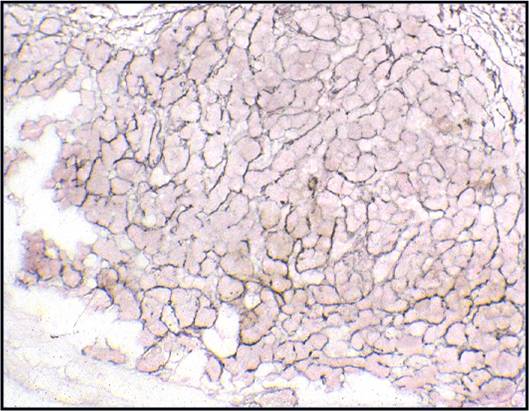
Regenerative, Dysplastic and Benign Neoplastic Hepatocellular Nodules – N12-12133 reactive, N12-4918 and N12-6339
- Hepatocytes arranged in jagged irregular clusters, small clusters, short rows and singly (depending on regenerative, dysplastic or neoplastic nature)
- No peripheral endothelium
- Clusters rarely have transgressing endothelium (except for neoplastic aspirates)
- Reactive hepatocytes show sibling polymorphism with normal nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio (1/3) and frequent binucleation
- Sporadically placed large, atypical cells with mild pleomorphism of nuclear size but normal nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio (in dysplastic hepatocytes with large cell change)
- Small uniformly monotonous hepatocytes with increased nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio and nuclear crowding (in dysplastic hepatocytes with small cell change)
- Variably prominent nucleoli but no macroeosinophilic nucleoli
- Cytoplasm is generally abundant (except in small cell change) and granular but may show fatty change, lipofuscin pigment, or iron deposition
- Bile duct epithelium present (except in LCA)
- Core biopsies provide specific diagnosis: Reticulin stain shows retention of 1 to 2 cells thick hepatic plate framework on cellblock; unpaired arterioles in parenchyma for LCA; bile duct proliferation and scar for FNH
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
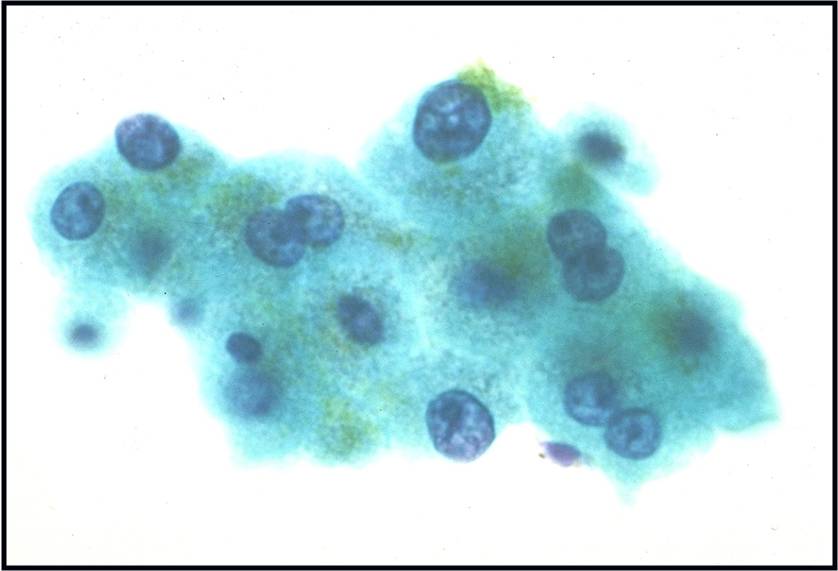
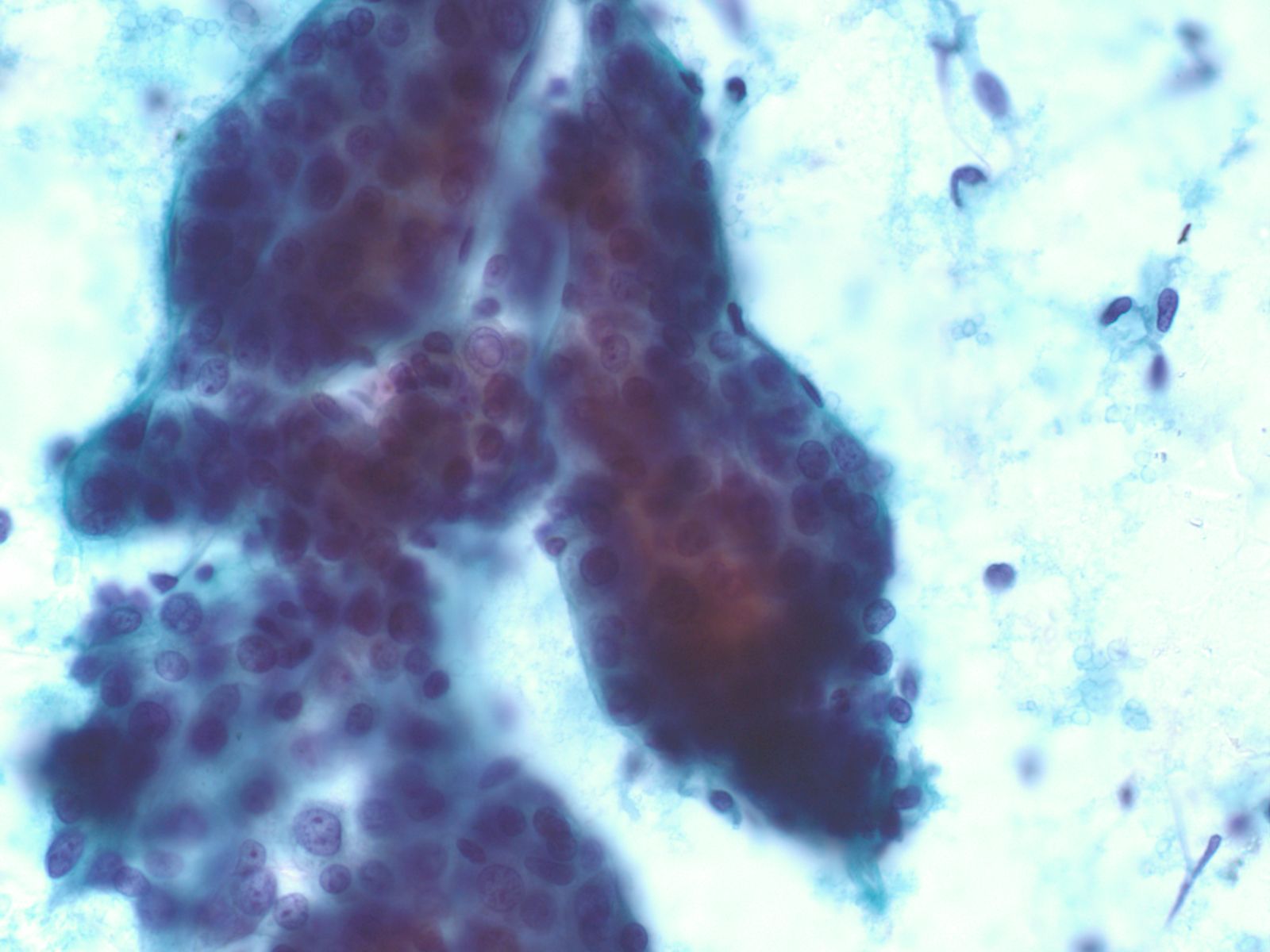
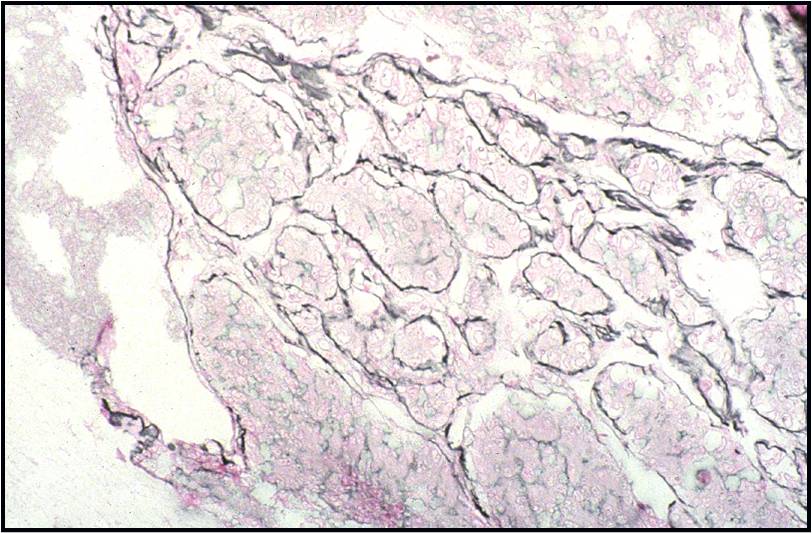
Well-differentiated Hepatocellular Carcinoma – N13-6335 and N12-5663
- Under low power microscopy, smear pattern shows trails of smooth-edged, arborizing clusters of thickened trabeculae with peripheral endothelium (pathognomonic)
- Under low power, smear pattern shows many loosely cohesive sheets of hepatocytes with transgressing vessels (highly suspect finding)
- Monotonous, uniform hepatocytic cell population with subtle malignant features
- Pseudoacinar formation in cell clusters
- Nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio higher than in normal hepatocytes (>1/3)
- Macroeosinophilic nucleoli
- Reduced number of binucleated cells
- Background free of bile duct epithelial cells
- Reticulin stain demonstrates a loss of the normal 1 to 2 cells thick hepatic plate architecture
- Iron stain fails to stain tumor cells in cases of hemochromatosis
- α-fetoprotein is helpful if positive but often is not
- Novel markers, such as glypican-3, glutamine synthetase and heat shock protein 70, are helpful if two out of three show positivity
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
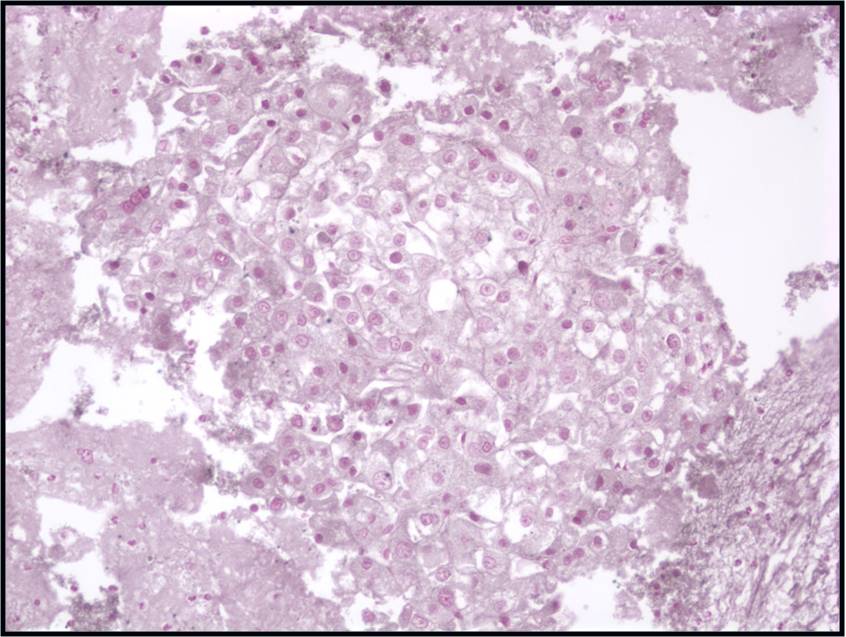
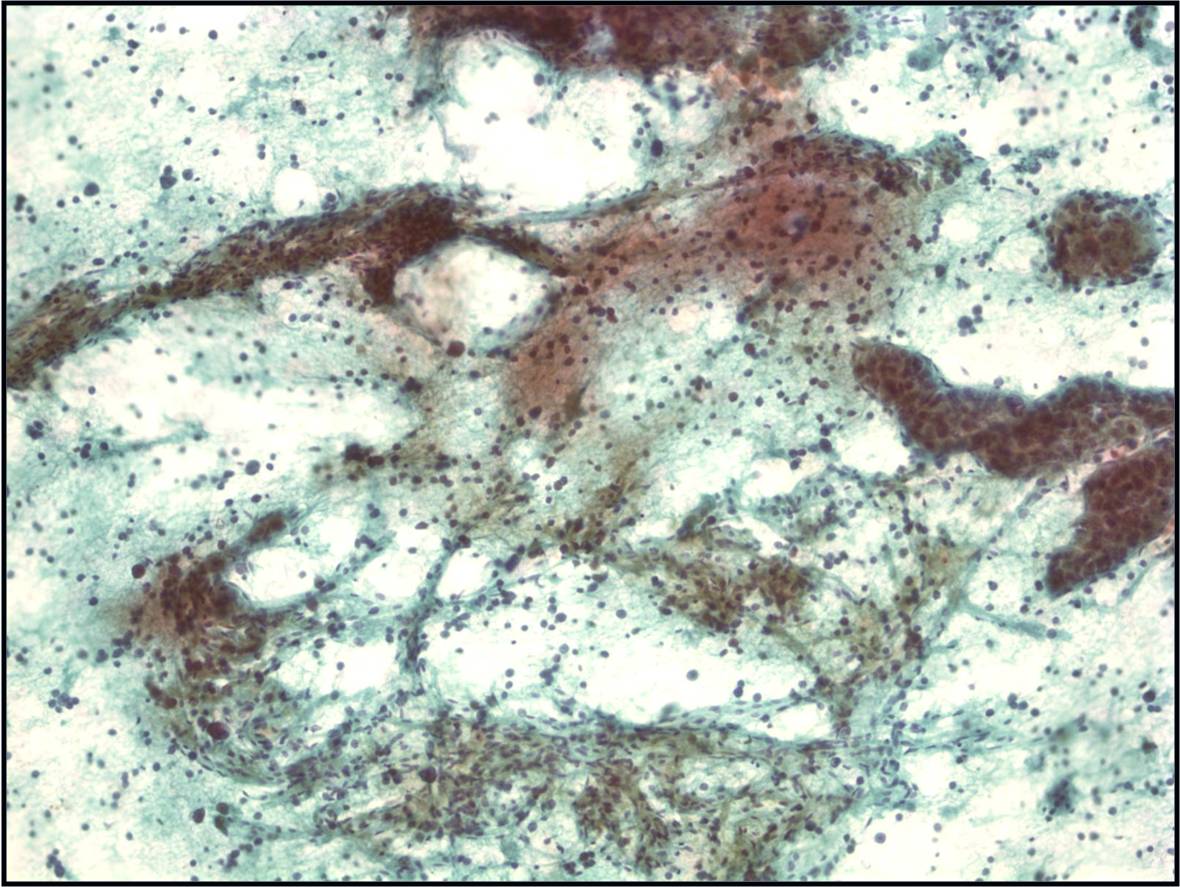
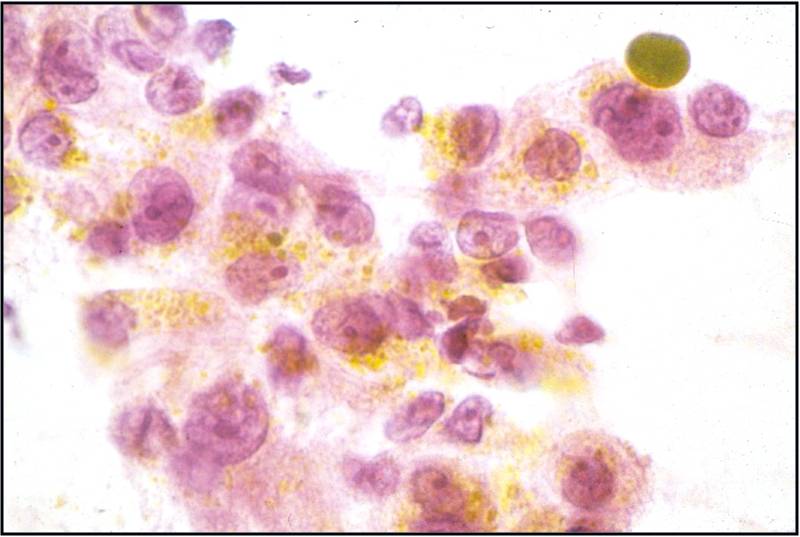
Moderately to Poorly Differentiated Hepatocellular Carcinoma –N12-6639, NC13-322 and N11-12944
- Low power smear pattern generally resembles that seen in well-differentiated tumors; however, there is a dyshesive tendency in poorly differentiated tumors
- Peripheral endothelium is virtually pathognomonic
- Transgressing vessels are suggestive, but cannot distinguish hepatocellular from renal cell carcinoma
- Presence of intracytoplasmic bile is pathognomonic
- Polygonal cells with central nuclei and prominent nucleoli with visible, granular to clear cytoplasm in moderately differentiated tumors; scant to no cytoplasm with greater degree of pleomorphism and mitotic activity in poorly differentiated tumors
- Immunophenotype: low-molecular-weight CK (Cam 5.2), polyclonal carcinoembryonic antigen and CD10 (canalicular), and HepPar-1 and TTF-1 positive; α-fetoprotein variable; high-molecular-weight CK (AE1) negative
 |
 |
|
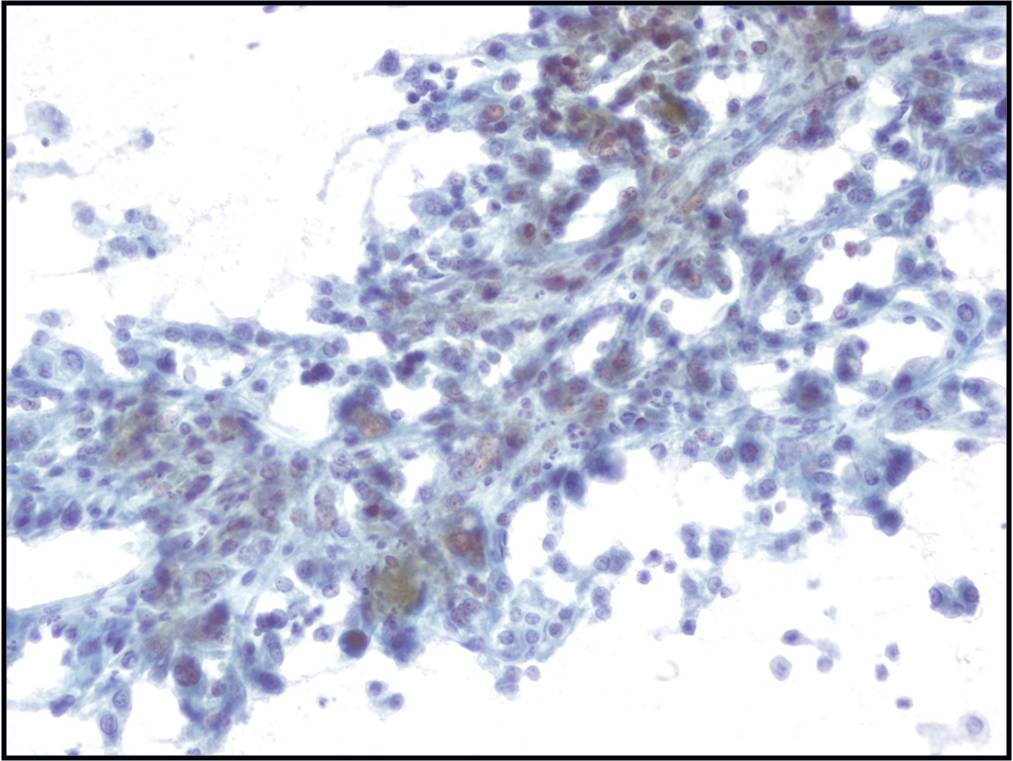
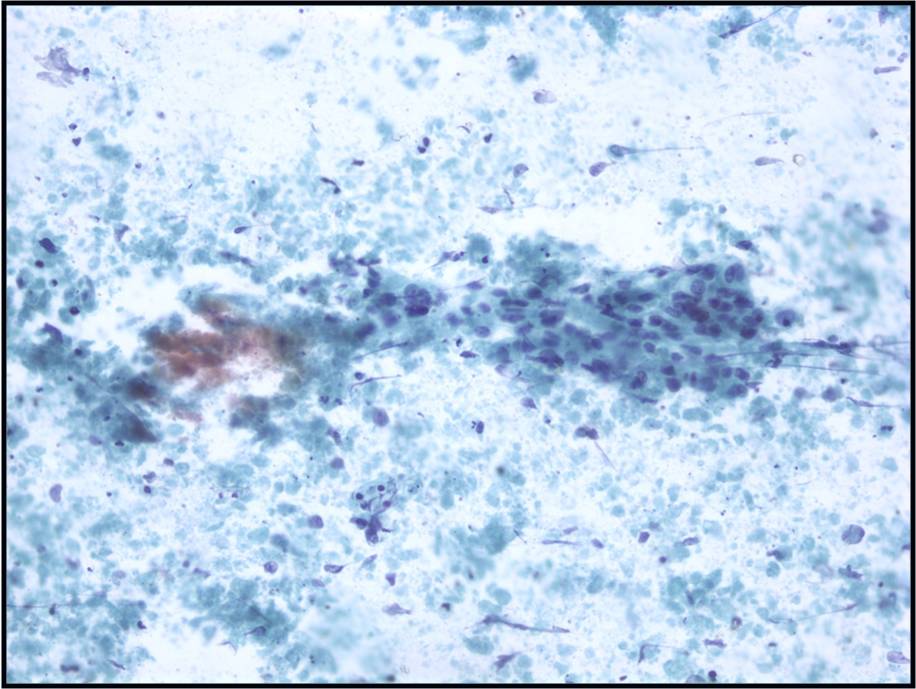
Metastatic colonic Adenocarcinoma -- N12-85
- Cigar-shaped, often palisaded nuclei
- Variably prominent nucleoli, no macroeosinophilic nucleoli
- Dirty necrosis in the background (key identification point)
- Immunohistochemistry: CK20 positive, CK7 and CK19 negative, carcinoembryonic antigen positive
 |
||